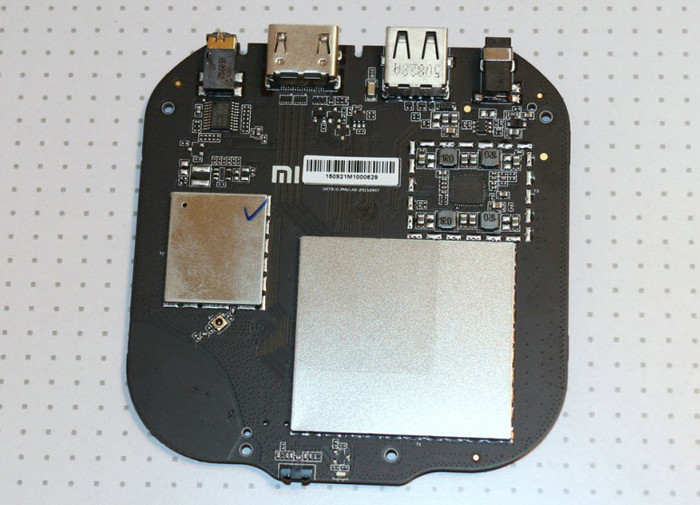
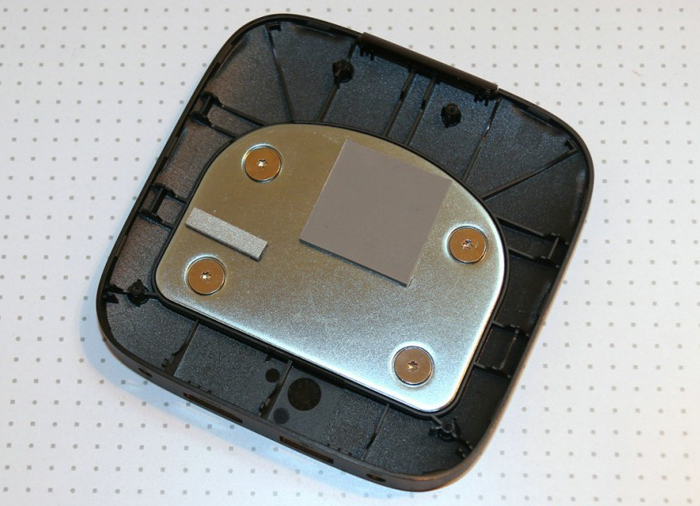
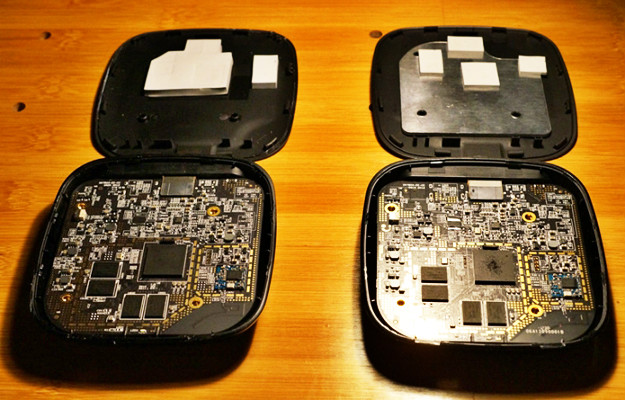
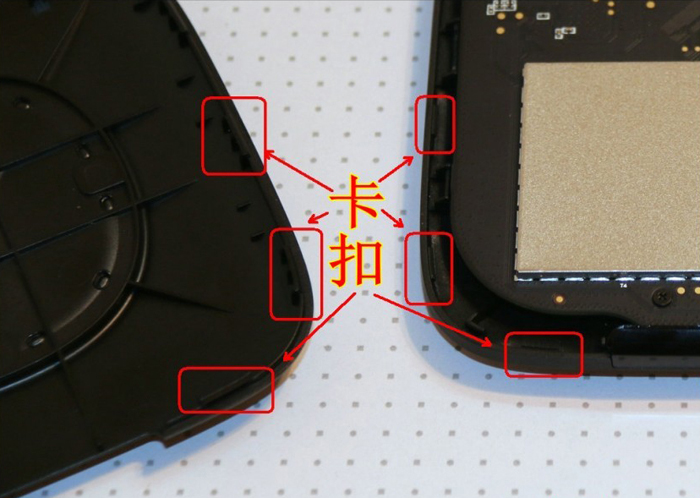



The shape of the millet box is simple and generous, and the outer casing is fixed and closed by some plastic buckles. After disassembling, you can completely see the internal electronic components and heat dissipation scheme of the box. It can be clearly seen that some thermal conductive silicone sheets are placed on the outer casing to transfer internal heat to the outer casing for heat dissipation. Generally speaking, household appliances are Heat will be generated during normal operation. If it is not conducted, the temperature of the electrical junction and electronic components will be too high, which will affect the efficiency, stability and service life of the product. The millet box will transfer the heat of the chip through the thermal silica gel gasket. By the way of natural convection heat dissipation to the outer casing, there is no need to worry about burning the millet box because the outer casing is too hot. At present, the heat of the millet box is normal, because the ARM chip itself is a low-power chip, even so, the chip surface may still have an operating temperature of no more than 70 degrees. The millet box itself, due to its size (probably with noise considerations), does not have a fan, but uses a heat sink. At the same time, its circuit board technology is relatively high, so if it is not higher than 70 degrees, it is generally not a problem.